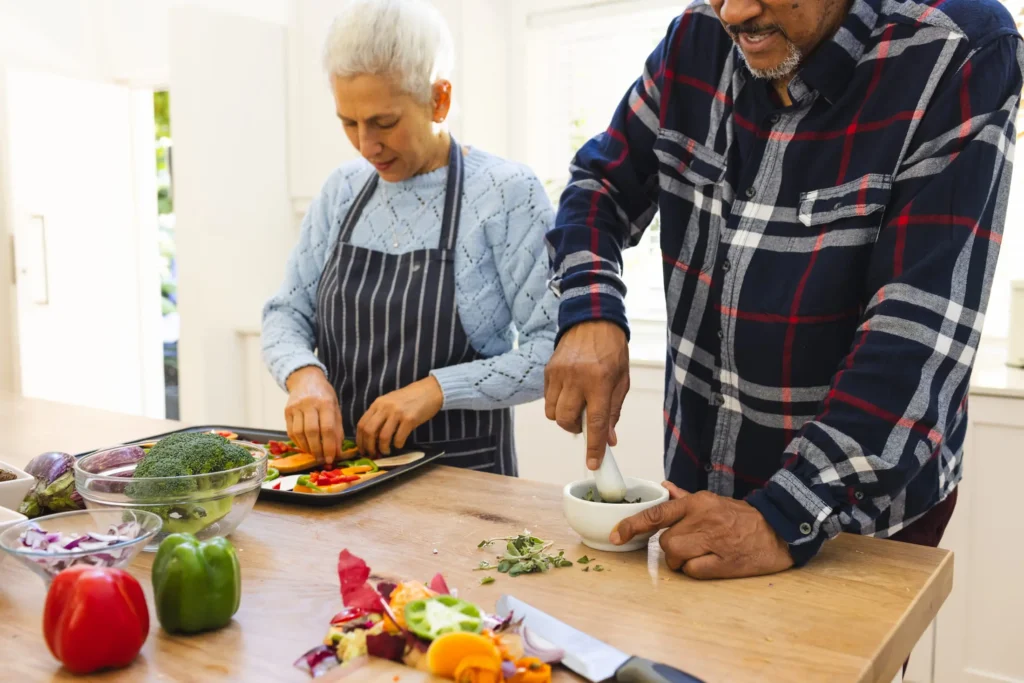
Properly organized nutrition at home supports clarity of thought, strengthens physical health, and brings inner peace, while also helping to save money. All it takes is a little time spent planning and a dash of creativity, and you’ll have delicious meals on your table that will delight both your body and soul. If you don’t know where to start, senior nutrition guidelines will help you create a healthy daily diet. Why Proper Nutrition Becomes More Important With Age Nutrition for aging adults is different, and wellness depends on it. It provides the body with essential vitamins and minerals, helping you feel productive and active. Changes in Metabolism and Muscle Mass With age, the body becomes more vulnerable to excessive calorie consumption. It can lead not only to excess weight, but also to the development of serious diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, gout, and the formation of stones in the kidneys and gallbladder. The recommended daily energy intake for older adults is approximately 2,100-2,300 kcal, and for older people, 1,900-2,000 kcal. If a person continues to work actively after retirement, their energy needs increase. The best indicator of the right balance is a stable muscle mass. Common Nutrient Deficiencies in Older Adults In older people, nutrient deficiencies can occur for various reasons, and their levels vary depending on individual characteristics. The most common contributing factors are: insufficient food intake and poor diet quality; age-related changes manifested in loss of appetite and forgetfulness; financial difficulties limiting the ability to buy healthy foods; taking medications that reduce nutrient absorption. A combination of physical, cognitive, and physiological changes can lead to the development of chronic diseases. A lack of essential nutrients worsens quality of life, reduces physical activity, and can lead to muscle loss and decreased bone strength, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. It, in turn, reduces strength, endurance, and immunity. Key Nutrition Guidelines for Seniors The main rule is to eat a varied diet. Get inspiration from recipes in books, on the internet, and from friends’ recommendations, and make sure you get the right balance of micronutrients. Area of Health Nutrition Focus Practical Advice Energy balance and metabolism Metabolism slows down with age, so avoid overeating. Control your portions, eat regularly, choose foods with a low glycemic index. Digestive wellness Fiber supports digestion and reduces the risk of constipation and high cholesterol Include vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains; aim for 25–30 g of fiber per day. Bone strength Calcium is required for bone reinforcement and osteoporosis prevention. Eat dairy products, green leafy vegetables, nuts; check your vitamin D levels. Muscle maintenance Protein helps maintain muscle mass, strength, and endurance Fish, eggs, lean meat, legumes; even distribution of protein throughout the day If you decide to create your own diet plan, first familiarize yourself with examples and recommendations from reliable sources. This will save you time and bring you closer to your goal of healthy eating at home. Building a Balanced Diet for Older Adults When planning meals for older people, it is essential to consider their health and personal taste preferences. A varied diet helps the body get all the necessary nutrients. A typical daily menu might look like this: oatmeal with fruit and green tea for breakfast, vegetable soup with steamed chicken breast and fresh vegetable salad for lunch, and baked fish with vegetables and a glass of kefir for dinner. Nutrition Tips for Managing Chronic Conditions In older people, taste perception gradually weakens, and many begin to use more salt and spices to compensate. However, remember that excess salt can retain fluid, increase the workload on the heart, and lead to hypertension. Dietary control is significant for seniors because their bodies no longer always allow them to eat what they want. Special diets are prescribed for stomach diseases, and soft foods are recommended for oral cavity problems. It is not a cause for concern, but simply a feature of aging that should be accepted. Stay hydrated. Drinking enough fluids helps prevent dehydration and many other problems. How to Support Healthy Eating Habits in Seniors Older people often have difficulty maintaining a balanced, nutritious diet on a regular basis. In such cases, dietary supplements can provide some support by helping to compensate for deficiencies in essential nutrients. It is important to remember that dietary supplements are not food in the strict sense of the word, so their use requires care and caution. Before purchasing any supplements, follow a few rules: understand that not every supplement is suitable for you; remember: even if the manufacturer claims that a product is “natural,” this is not always true; some supplements can cause unwanted side effects; if you are taking medication, supplements can alter its effect — either weakening or strengthening it. never use supplements to treat or diagnose diseases without first consulting your doctor. Healthy aging nutrition should be based on a balanced diet, and supplements should only be used as an additional tool under the supervision of a specialist. When to Consult a Registered Dietitian Consulting a nutritionist is always the right solution. They will send you for a health check-up to identify any vulnerabilities. Understanding protein requirements for elderly people will enable you to create a healthy diet, improve your well-being, and enhance your health.